History and the Biblical Account
Found 11 Search results
Avoiding Another Kadesh Barnea
Rabbi David SilverbergMoshe’s history lesson is designed to avoid a repetition of the sin of the spies. To this end, the conquering of the Emmorite kings is described as premeditated and the tension regarding the Eastern tribes is downplayed. The commentators offer various explanations as to the relationship of the appointing of judges to the sin of the spies.
Rehavam: Three Sources - Three Perspectives
Rabbi Alex IsraelThe description of Rehavam in Melakhim focuses on the sin of idolatry and on the Mikdash in Jerusalem. In Divrei Hayamim the focus is on the sin of pride and has a broader regional focus. Archaeological evidence testifies that Shishak attacked Yerovam in the North. This is not mentioned in either of the bibical accounts. What is the relationship between the various accounts and what is the relationship between the biblkical account and history?
The Historical Context of Megillat Esther
Prof. Jonathan Grossman and Rabbi Dr. Yehoshua ReissThe historical context of the story is investigated and reveals a tension between the Jews who returned to Eretz Yisrael and the Jews who stayed in Shushan.
Megillat Esther - Questions for Self Study
Rabbi Menachem LeibtagThese self-study questions will prepare you for this series of lessons about Megillat Esther. The qustions deal with the historical background of Megillat Esther and the relationship between Megillat Esther and Sefer Zekharya.
Megillat Esther and Sefer Zekharya
Rabbi Menachem Leibtag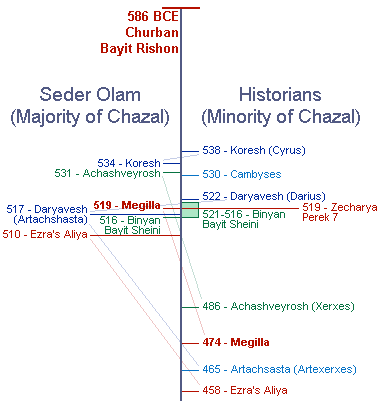
According to the chronology posited by Seder Olam, Ahashveyrosh was the king immediately after Cyrus but before Darius, and the story of Megillat Esther immediately led to the building of the second Beit HaMikdash and a mass Aliya. However, according to the common historical approach Ahashverosh was the king who succeeded Darius. The Beit HaMikdash was already built and two decades pass before any new Aliya movement. In fact, no major event takes place immediately after the events in Megillat Esther. However, parallels between Megillat Esther and the prophecies of Zekharya imply that the initiators of the holiday of Purim understood that the ultimate success of the Return to Zion and the rebuilding of the Beit HaMikdash depended on the implementation of social Mitzvot.
The Fall and Rise of Yisrael
Rabbi Alex IsraelDuring Yehu's reign Aram, headed by Hazael occupy the Eastern bank of the Jordan. In Yehoahaz's time the situation becomes direr as Aram imposes a full demilitarization of Israel. The turnaround begins in the days of Yoash who receives a deathbed prophecy from Elisha of a victory over Aram and peaks in the time of Yerovam ben Yoash who receives a prophecy from Yona ben Amitai and restores the Northern border to a magnitude previously witnessed only during the days of David and Shlomo. While historians describe the decline of Aram due to the rise of Assyria, the book of Kings describes a divine process which is surprisingly almost entirely devoid of any repentance.
Does the outcome of the prophetic action that Elisha preforms with Yoash on his deathbed actually have an impact on the outcome in reality?
Is the resurrection from death of the man who came in contact with Elisha's buried bones just another miracle of Elisha or does it symbolize a national resurrection?
Sanheriv’s Siege of Jerusalem
Rabbi Alex IsraelHizkiyahu takes advantage of a gap in Assyrian rule and joins Egypt and Babylon in rebellion against Assyria. He fortifies Jerusalem and channels water into the walled city, while cutting off the water supply outside of the city. However, the new Assyrian king Sanheriv fights back, destroying 46 fortified cities in Yehuda, and sets his sights on Jerusalem. Sanheriv sends emissaries to Jerusalem to deflate the moral of the people and encourage them to surrender while boasting that God cannot stop him. After Yishayahu first prophecy sends Sanheriv away temporarily, Sanheriv returns to Jerusalem once again. This time Hizkiyahu prays to God and miraculously the entire Assyrian army is killed in one night. This description has an indirect corroboration in Assyrian historical documents that describe the war against Hizkiyahu in a manner which is jarringly inconsistent with other battles. This miracle led to the concept of Jerusalem's invincibility, a concept that the prophet Yirmiyahu could not change when he prophesied its destruction over a century later.
The Beginning of the End
God’s Sword in the Hand of the King of Babylon - Part 2
Dr. Tova GanzelThis article provides historical background about the king of Babylonia, Nevukhadnetzar and contrasts how he was seen by the two major prophets of his time, Yirmiyahu and Yehezkel. Additionally, this article examines life in the Babylonian exile, based on extra-biblical sources.
Prophecies to Egypt
Dr. Tova GanzelEgypt’s long-term stability in the region, its geographic proximity, and its historic connection with Israel form the foundation of Yehezkel’s prophecies to this country. The prophet points an accusing finger at Egypt in three areas:
The first and most central accusation, common to Tzor and Egypt, is the sin of arrogance towards God. The kings of Tzor and of Egypt attribute their successes to themselves. They pride themselves on their successes, boast about them, and scorn the God of Israel. However, the prophet assures Egypt that even when the Temple is in ruins and God’s nation is exiled, it is God Who determines the fate of all nations, including Egypt, and its king.
This was a period when Egypt hoped to become a superpower with influence beyond the region, following the fall of Assyria and prior to Babylon reaching its zenith. Therefore, Egypt encouraged Tzidkiyahu to rebel against Babylon which ultimately brought upon the downfall of Yehuda. Yehezkel’s prophecies put an end to the possibility of an Egyptian empire, not only in the worldly realm, but also from the Divine perspective. From now onwards, as in the past, Egypt will be a “lowly kingdom,” not an empire.
Finally, Egypt is accused of the religious harlotry that infiltrated Israel.
Tanakh and Archaeology
Part 5 - The Exodus
Rabbi Amnon BazakUntil recently, doubts as to the veracity of the story of the exodus were rejected out of hand by most biblical scholars in Israel for two reasons:
- The unlikeliness that a people would invent a tradition of subjugation at the very outset of their existence.
- The many mentions of the Exodus from Egypt in the Bible as a central event in the life of the nation.
Nevertheless, the arguments that are raised against the veracity of the Biblical story of the Exodus and deny the servitude in Egypt are based on various claims of lack of evidence and instances of anachronism.
It must be emphasized that theories based on a lack of evidence must be treated with much reservation. As to the absence of any mention of the exodus in Egyptian records, we must take into account that kings of the ancient world, including the pharaohs, used to construct monuments glorifying their victories and achievements, not their defeats and failures.
In the case of the exodus there is proof that the narrator possesses extensive knowledge about the details of the period in question, and especially the sort of details that changed in later times. Had the biblical account indeed been written only in the 7th century B.C.E, it hardly seems likely that the narrator could integrate such precise details of Egyptian reality some six hundred years prior to his or her own time.
Archaeology and the Exodus from Egypt
Rabbi Amnon Bazak

